Future-Proof Your Finances: How to Get Pre-Qualified for a Personal Loan
Facing the world of personal loans can be a daunting experience, but pre-qualifying for a personal loan is the first step towards securing your financial future. Understanding the process and its significance equips you to make informed decisions and improve your chances of obtaining favorable loan terms.
Understanding the Importance of Pre-Qualification
What is Pre-Qualification?
Pre-qualification is the initial assessment of your financial profile by lenders before you formally apply for a personal loan. It involves providing basic information about your income, assets, and existing debts, which lenders use to evaluate your creditworthiness and determine your eligibility for a loan.
Benefits of Getting Pre-Qualified for a Personal Loan
Getting prequalify for a personal loan offers several advantages:
- Financial Check-Up: The pre-qualification process acts as a comprehensive financial check-up, highlighting areas that may need improvement before applying for a loan.
- Improved Creditworthiness: By addressing any potential issues identified during pre-qualification, you can enhance your creditworthiness and appeal to lenders.
- Better Loan Terms: A strong financial profile can lead to more favorable loan terms, including lower interest rates and better repayment periods.
- Time and Effort Savings: Pre-qualifying for a personal loan helps you avoid applying for loans you're unlikely to qualify for, saving you time and effort.
Steps to Get Pre-Qualified for a Personal Loan
Step-by-Step Process Overview
Getting pre-qualification personal loan typically involves the following steps:
- Gather Necessary Documents: Collect essential documents such as pay stubs, tax returns, bank statements, and proof of employment.
- Check Your Credit Score: Review your credit report and credit score to identify any potential issues or errors that need to be addressed.
- Calculate Your Debt-to-Income Ratio: Determine your debt-to-income ratio by dividing your total monthly debt payments by your gross monthly income.
- Submit Your Information to Lenders: Provide the requested information to potential lenders, either online or in person, for the pre-qualification process.
- Review Pre-Qualification Offers: Evaluate the pre-qualification offers from different lenders, comparing interest rates, loan terms, and other factors.
- Negotiate (if Necessary): If you receive multiple pre-qualification offers, you may have the opportunity to negotiate better terms with lenders.
Pre-qualification for a personal loan is a straightforward process that empowers you to assess your loan eligibility and explore potential terms, helping you make informed decisions. By following these to get prequalified for a personal loan, you can gather the necessary information, submit your details to lenders, and receive preliminary loan offers. This valuable insight enables you to compare options and select the lender that best aligns with your financial goals.
Documentation and Information Required
To streamline the pre-qualification process, it's essential to have the following documentation and information ready:
- Proof of income (pay stubs, tax returns, etc.)
- Employment verification (job title, employer name, etc.)
- Identification documents (driver's license, Social Security number, etc.)
- Existing debt obligations (credit card statements, loan statements, etc.)
- Assets (bank statements, investment accounts, etc.)
By organizing and presenting these documents efficiently, you can ensure a smoother pre-qualification experience and improve your chances of receiving accurate loan offers.
Evaluating Your Financial Health
Credit Score Analysis
Your credit score plays a critical role in the pre-qualification process, as it provides lenders with a snapshot of your creditworthiness. A higher credit score typically translates to better loan terms and a higher likelihood of approval.
Here's how credit scores are generally categorized:
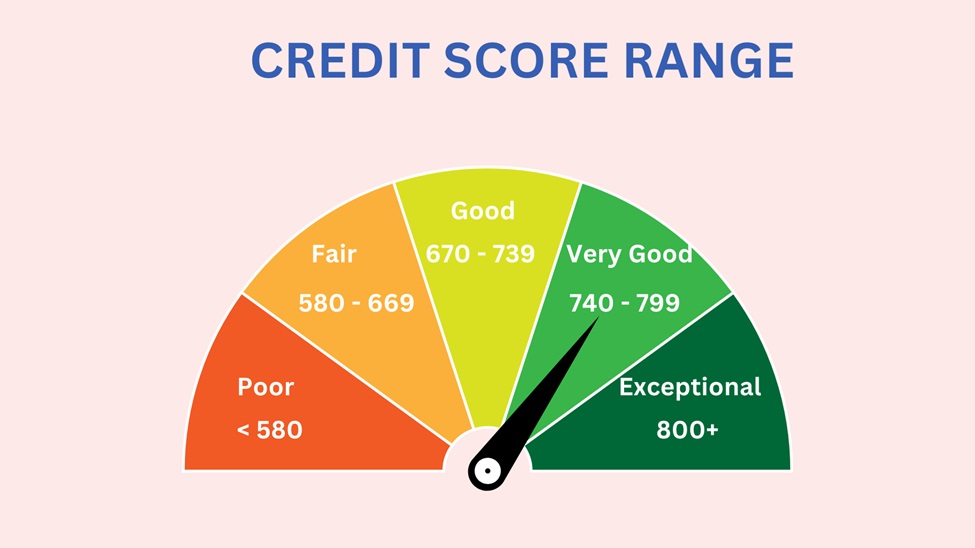
To improve your credit score before applying for a personal loan, consider the following strategies:
- Pay Bills on Time: Payment history is the most significant factor affecting your credit score. Make sure to pay all your bills on time.
- Reduce Debt: High credit card balances and other outstanding debts can negatively impact your credit score. Work on paying down debt to improve your credit utilization ratio.
- Dispute Errors: Review your credit report for any errors or discrepancies, and dispute them with the credit bureaus to have them corrected.
Debt-to-Income Ratio
Your debt-to-income ratio (DTI) is another crucial factor that lenders consider when evaluating your financial health. It represents the percentage of your gross monthly income that goes towards paying off debts.
To calculate your DTI, divide your total monthly debt payments (credit card bills, loan payments, etc.) by your gross monthly income. For example, if your monthly debt payments total $2,000 and your gross monthly income is $6,000, your DTI would be 33% ($2,000 ÷ $6,000 = 0.33).
Generally, lenders prefer a DTI of 36% or lower for personal loans, although some may accept higher ratios depending on your overall financial profile.
To improve your debt-to-income ratio, consider the following strategies:
- Increase Your Income: Look for opportunities to increase your income through a job promotion, side gig, or additional employment.
- Pay Down Debts: Focus on paying down existing debts, particularly those with high interest rates, to reduce your monthly debt obligations.
- Consolidate Debts: Consolidating multiple debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate can help reduce your monthly payments and improve your DTI.
Choosing the Right Lender
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Lender
When evaluating personal loan lenders, consider the following factors:
- Interest Rates: Compare the interest rates offered by different lenders to find the most competitive option.
- Loan Terms: Evaluate the repayment period and ensure it aligns with your financial goals and ability to make payments.
- Lender Reputation: Research the lender's reputation, customer reviews, and complaint history to gauge their reliability and customer service.
- Additional Fees: Be aware of any origination fees, prepayment penalties, or other charges that may impact the overall cost of the loan.
Negotiating with Lenders
While pre-qualification offers provide an initial glimpse into potential loan terms, it's essential to remember that these terms are often negotiable. Here are some tips for negotiating with lenders:
- Compare Offers: If you've received multiple pre-qualification offers, use them as leverage to negotiate better terms with your preferred lender.
- Highlight Your Strengths: Emphasize your strong financial profile, such as a high credit score, stable income, and low debt-to-income ratio, to demonstrate your creditworthiness.
- Be Prepared to Walk Away: If a lender is unwilling to meet your desired terms, be prepared to walk away and explore other options.
- Consider Alternative Lenders: Traditional banks may offer less flexibility than online lenders or credit unions, which could be more open to negotiations.
Remember, negotiation is a skill, and being prepared with knowledge and reasonable expectations can increase your chances of securing favorable loan terms.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Pre-Qualification
While the pre-qualification process is designed to streamline your personal loan application process, several common mistakes can derail your efforts:
Overlooking Eligibility Requirements
Many lenders have specific eligibility requirements for personal loans, such as minimum credit scores, income thresholds, or debt-to-income ratio limits. Failing to meet these requirements can result in an automatic rejection, even if you've been pre-qualified.
To avoid this mistake, thoroughly review the lender's eligibility criteria before proceeding with the pre-qualification process.
Ignoring Total Loan Costs
When evaluating personal loan offers, it's easy to focus solely on the advertised interest rate (APR). However, this can lead to overlooking other costs associated with the loan, such as origination fees, prepayment penalties, and late payment charges.
To accurately assess the total cost of a loan, consider the following factors:
- Origination Fees: Lenders may charge an upfront origination fee, which is typically a percentage of the loan amount. This fee can significantly increase the overall cost of the loan.
- Prepayment Penalties: Some lenders impose penalties if you pay off the loan early. These penalties can offset the savings you might have achieved by paying off the loan ahead of schedule.
- Late Payment Fees: Most lenders charge late payment fees, which can add up quickly if you miss multiple payments.
To calculate the total cost of a loan, use an online loan calculator or consult with a financial advisor to ensure you have a comprehensive understanding of the expenses involved.
FAQs: Addressing Key Questions
1. What is the difference between a pre-qualified and pre-approved personal loan?
Pre-qualification and pre-approval are two distinct stages in the loan application process, and it's crucial to understand the differences:
Pre-qualification: This initial step involves providing basic financial information to lenders, who then evaluate your creditworthiness and provide an estimate of the loan amount and terms you may qualify for. However, pre-qualification does not guarantee loan approval.
Pre-approval: Pre-approval is a more in-depth process that involves a lender thoroughly reviewing your financial documents, credit history, and other relevant information. If you meet the lender's criteria, you'll receive a conditional commitment for a specific loan amount and terms, subject to final verification and approval.
While pre-qualification is a helpful starting point, pre-approval carries more weight and increases your chances of securing the desired loan.
2. Can pre-qualification affect my credit score?
Pre-qualification typically involves a soft credit inquiry, which does not impact your credit score. However, if you decide to proceed with a formal loan application after pre-qualification, the lender will likely conduct a hard credit inquiry, which can temporarily affect your credit score.
It's important to note that multiple hard inquiries within a short period can have a more substantial impact on your credit score. Therefore, it's advisable to limit the number of formal loan applications you submit.
3. How often should I get personal loans pre-qualify if I haven't decided on a loan yet?
If you're not ready to commit to a personal loan, it's generally recommended to get pre-qualified every six months to a year. This frequency allows you to monitor any changes in your financial situation and ensures that the pre-qualification information remains up-to-date.
However, if you experience significant life events or changes to your income, employment, or credit profile, it's advisable to get pre-qualified again sooner to ensure accurate information for potential lenders.
By understanding the pre-qualification process and its nuances, you can take proactive steps to future-proof your finances and increase your chances of securing a personal loan with favorable terms. Remember, preparation and awareness are key to navigating the lending landscape successfully.

