Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
Tigera
Achieving CI Velocity at Tigera using Semaphore
Tigera serves the networking and policy enforcement needs of more than 150,000 Kubernetes clusters across the globe and supports two product lines: open source Calico, and Calico Enterprise. Our development team is constantly running smoke, system, unit, and functional verification tests, as well as all our E2Es for these products. Our CI pipelines form an extremely important aspect of the overall IT infrastructure and enable us to test our products and catch bugs before release.
Self-Service Network Security for Kubernetes
Calico and K8s Network Policies - An Overview and Comparison
The New Model for Network Security: Zero Trust
The old security model, which followed the “trust but verify” method, is broken. That model granted excessive implicit trust that attackers abused, putting the organization at risk from malicious internal actors and allowing unauthorized outsiders wide-reaching access once inside. The new model, Zero Trust networking, presents an approach where the default posture is to deny access.
Mitigating the Risks of Instance Metadata in AWS EKS
Compromising a pod in a Kubernetes cluster can have disastrous consequences on resources in an AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) account if access to the Instance Metadata service is not explicitly blocked. The Instance Metadata service is an AWS API listening on a link-local IP address. Only accessible from EC2 instances, it enables the retrieval of metadata that is used to configure or manage an instance.
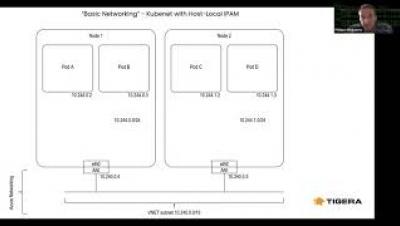
Getting up and running with Calico on AKS
Visibility and Troubleshooting Modern Applications with Calico Enterprise and OpenShift
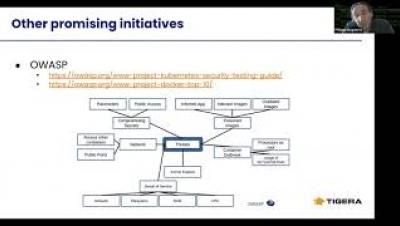
Security Policy Self-Service for Developers and DevOps Teams
In today’s economy, digital assets (applications, data, and processes) determine business success. Cloud-native applications are designed to iterate rapidly, creating rapid time-to-value for businesses. Organizations that are able to rapidly build and deploy their applications have significant competitive advantage.