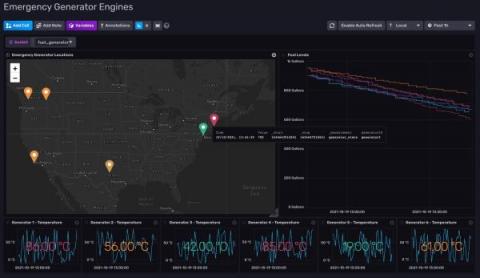
InfluxDB and GeoData - Emergency Generators
With the widespread use of LTE (Long Term Evolution), we are seeing more IoT devices come online in remote regions of our planet. Picture this scenario: A country is currently experiencing a national emergency due to an electrical grid failure. To mitigate the power shortage the government has deployed generators in the remote regions of their country to power the most remote villages. The problem? The villages are still reporting outages due to the emergency generators running out of fuel.