Getting Hands on with Harvester HCI
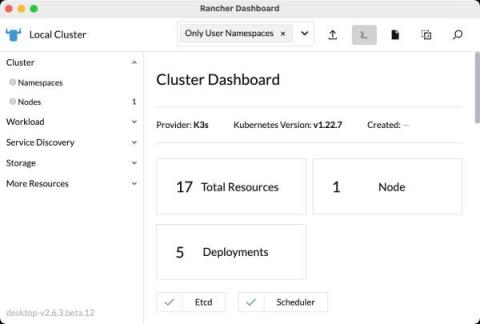
When I left Red Hat to join SUSE as a Technical Marketing Manager at the end of 2021, I heard about Harvester, a new Hyperconverged Infrastructure (HCI) solution with Kubernetes under the hood. When I started looking at it, I immediately saw use cases where Harvester could really help IT operators and DevOps engineers. There are solutions that offer similar capabilities but there’s nothing else on the market like Harvester.