Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
Latest Posts
Kubernetes vs YARN for scheduling Apache Spark
Spark is one of the most widely-used compute tools for big data analytics. It excels at real-time batch and stream processing, and powers machine learning, AI, NLP and data analysis applications. Thanks to its in-memory processing capabilities, Spark has risen in popularity. As Spark usage increases, the older Hadoop stack is on the decline with its various limitations that make it harder for data teams to realize business outcomes.
Creating a Better Incident Response Plan
Why Should My Business Consider Private And Direct Connections To Oracle Cloud?
New: Dashboard Server Enterprise version
In April, we brought you the ability to dashboard any data with the new SquaredUp Dashboard Server product – for free. Then at SquaredUp Live, we announced the launch of Dashboard Server Enterprise for enterprise organizations who have got to grips with their dashboarding and now want to scale up. You can purchase unlimited named users and get endless data connections plus new, enterprise integrations that let you dashboard just about anything.
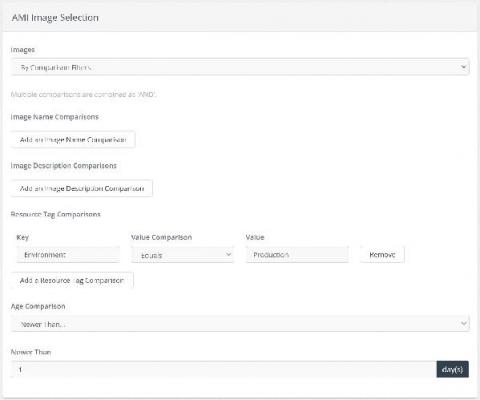
Copy AMI Images to S3 Actions
It is very important to create backups for your crutial EC2 instances. While AWS provides mechanisms to increase availability, the cloud is not infallible. EC2 provides a native backup format for your EC2 instances in the way of AMI images. But storage costs of the AMI images can build over time.
Continuous integration with GitOps
Software development is changing rapidly. On one hand, you must quickly adapt to evolving requirements, while on the other, your applications need to operate continuously without downtime. DevOps helps you quickly adapt to changes. Among other initiatives, continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD) are intgegral to any DevOps practice.
Preventing SQL injection attacks with automated testing
SQL injection is one of the most destructive ways an application can be attacked. This kind of attack is targeted toward the application database, which can result in consequences that are irreversible, lead to loss of money, and reduce user trust in your company. There are far too many application data breaches happening every day, usually when a malicious agent attacks the database.
What is the Coralogix Security Traffic Analyzer (STA), and Why Do I Need It?
The wide-spread adoption of cloud infrastructure has proven to be highly beneficial, but has also introduced new challenges and added costs – especially when it comes to security. As organizations migrate to the cloud, they relinquish access to their servers and all information that flows between them and the outside world. This data is fundamental to both security and observability.