Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
Latest News
When to choose a Layer 2 or Layer 3 connection to connect to your cloud
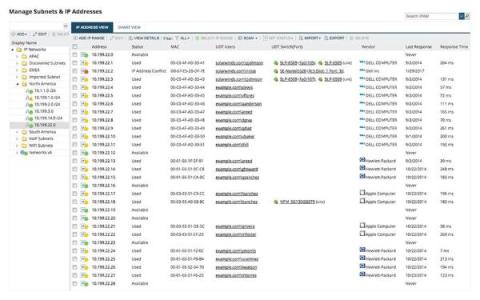
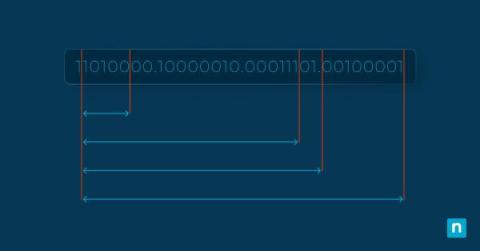
Subnetting - Ultimate Guide - Definition, How & Why?
Using VPC Flow Logs to Monitor AWS Virtual Public Cloud
How to Deploy Microsoft LAPS
Securing privileged accounts is of utmost concern to cybersecurity professionals, and Active Directory, Microsoft’s identity and access management service, forms the backbone of the majority of organizations. Active Directory (AD) centralizes user accounts, computers, and resources, ensuring access control, and local administrator accounts wield substantial power within Windows systems.
What Is IPv6? Definition & Full Overview
Poised to redefine the landscape of digital communication stands the groundbreaking achievement that is IPv6, the sixth generation of the Internet Protocol. The evolution from IPv4 to IPv6 marks a pivotal shift in internet technology, driven by the increasing scarcity of IPv4 addresses and the expanding scale of the global network.
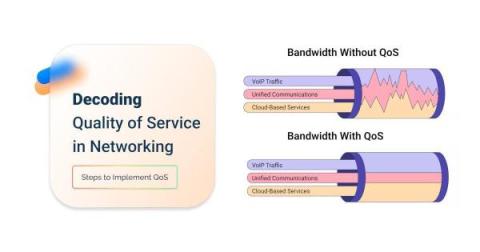
What is QoS in Networking: Decoding Quality of Service
What Is CIDR? Classless Inter-Domain Routing Explained
In the early 1990s, as the digital world stood on the cusp of an explosive expansion, the foundational structure of the internet faced a critical challenge: the classful IP addressing system was buckling under its own rigidity and inefficiency. Locked into fixed classes (A, B, and C), this system squandered valuable IP space, leaving the burgeoning network gasping for air as it grappled with rapidly depleting IP addresses.
How to Install and Set up a VPN on Windows Server 2022
A VPN, or Virtual Private Network, enables secure communications over an untrusted network. It enables users to connect to servers and networks from virtually anywhere, creating a secure tunnel between the user and a remote network or server. VPNs ensure data privacy and prevent unauthorized access, ensuring the data transmitted remains confidential and protected from external threats.
Rate limiting based on AWS VPC ID
Managing incoming web traffic for your applications is essential to ensuring optimal performance, preventing abuse, and maintaining the security of your cloud infrastructure. To accomplish this, one of the tools HAProxy Enterprise users have at their disposal is rate limiting—the practice of preventing clients from making too many requests and using system resources unfairly.