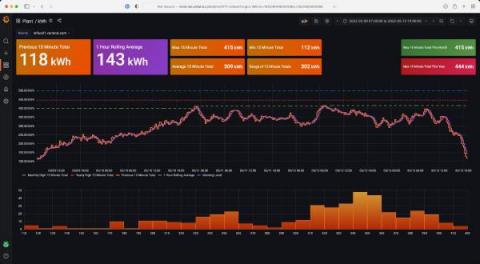
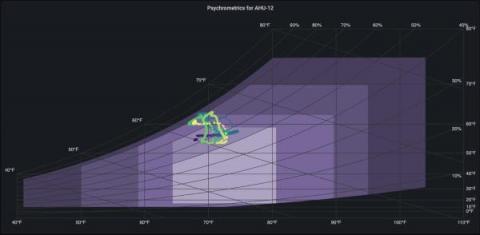
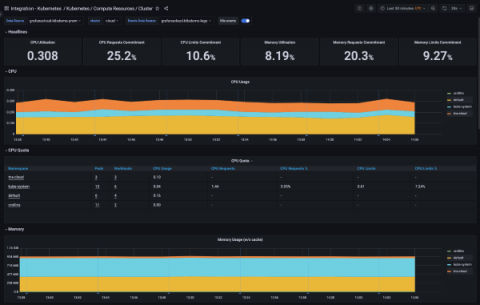
Reduce MTTR and improve UX with Grafana Enterprise: Inside Optum's observability stack
Among the 12 greatest stressors in life, six revolve around healthcare issues. From loss of a loved one to pregnancy and even retirement, these events often involve interactions with healthcare services — interactions that can either add to an individual’s stress or, ideally, help alleviate it.