Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
Site24x7
10 filter patterns that are helpful for managing your logs
Log files, which are the records of everything that has happened in your server, application, or framework, are generally unfiltered and huge. Going on for pages, these plain text files are packed with tons of information and are the initial go-to place for any troubleshooting. However, the challenge lies in reading, understanding, and interpreting log files, and ultimately pulling out the right piece of information required for analysis.
Service Maps: The guide to your application architecture
[Webinar] Five cloud cost management strategies that work
[Webinar] Reduce calls to help desk using status pages
Communicate incidents in real-time with StatusIQ
Site24x7 Server Monitoring: Your pit stop for capturing the disk monitoring flag
All storage devices, whether on-premises or in the cloud, are used to store or maintain data in a server. To organize files based on usage and perform read/write operations, the disk is divided into separate portions called partitions. A partition can contain the entire disk space or some of it. Disk usage gives the amount of space used by the storage device to read/write an operation.
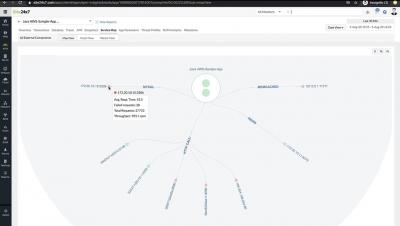
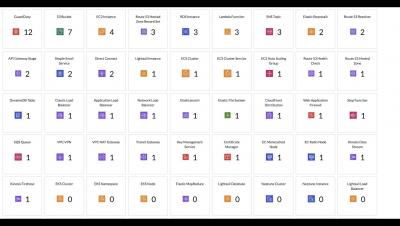
Uptime monitoring for your AWS resources
Why HTTPS is important for your website security
HTTP, which stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol, is a communication protocol used by your browser to connect to the web server of the site you're looking for. When HTTP data transfer between the browser and the web server is shared via unencrypted hypertext, anybody connected to your network can intercept the data you're transferring. To combat this, it's best to switch to HTTPS, the more secure extension of HTTP. You can't verify data integrity with HTTP