Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
Analytics
Smarter Digital Payment Monitoring to Protect Business Operations
You place your mug on your desk and boot your computer. Like every morning, you skim over various dashboards on one screen and sift through your email alerts on the other before you start pulling the regular reports. But this morning turns out to be nothing like other mornings. It is about to take a mean twist that will keep you from ever finishing your morning coffee.
Winning with Developer Experience
Start using OpenSearch with NodeJS
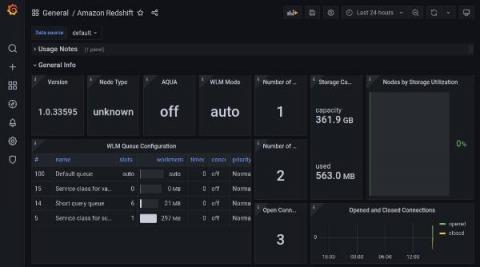
Monitor all your Redshift clusters in Grafana with the new Amazon Redshift data source plugin
In collaboration with the AWS team, we have recently released the new Redshift data source plugin for Grafana. Amazon Redshift is the fastest and most widely used cloud data warehouse. It uses SQL to analyze structured and semi-structured data across data warehouses, operational databases, and data lakes by using AWS-designed hardware and machine learning.
MQTT Topic and Payload Parsing with Telegraf
Buckle up, this one isn’t short…but I’m hoping it will be thoroughly informative! This post is about Telegraf as a consumer of MQTT messages in the context of writing them to InfluxDB. If you are interested in and unfamiliar with Telegraf, you can view docs here. Unsure if Telegraf aligns with your needs? I make a case for it in the Optimizing Writes section of this blog post. It may also help to have an understanding of Line Protocol, InfluxDB’s default accepted format.
How to scale your business with the Aiven Cluster startup program
Announcing Apache Cassandra 4.0
UKCloud announces Strategic Partnership with Data Virtualisation Leader Denodo
Data Pipelines Overview
A Data Pipeline is a series of processes that collects raw data from various sources, filters the disqualified data, transforms them into the appropriate format, moves them to the places you want to store them, analyzes them, and finally presents them to your audience. As we can see in the chart above, a data pipeline is analogous to a water flow: data flows from one stage to another while being processed and reshaped.