Dashboards
How to monitor pool water levels from anywhere with Grafana
I’ve had a swimming pool at my house in Massachusetts since 2016. One of the problems that pool owners like myself face when we go on vacation or leave for several days is evaporation from the pool and the water level dropping below the skimmers. This can happen due to sunlight and warm temperatures. It can also happen when temperatures drop at night and the pool is being heated — the water temperature is warmer than the air, causing the water to evaporate.
Observing the Internet of Things (Grafana Office Hours #08)
What's new in k6 browser? (k6 Office Hours #98)
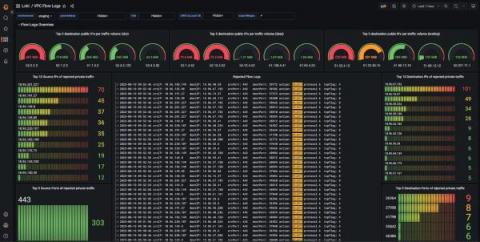
How Qonto used Grafana Loki to build its network observability platform
Christophe is a self-taught engineer from France who specializes in site reliability engineering. He spends most of his time building systems with open-source technologies. In his free time, Christophe enjoys traveling and discovering new cultures, but he would also settle for a good book by the pool with a lemon sorbet.
Understanding Grafana k6: A simple guide to the load testing tool
Grafana k6 is a powerful, developer-friendly tool designed and engineered with a focus on load testing — but it boasts capabilities that extend far beyond that use case. Understanding the inner workings of k6 is helpful to fully leverage its potential, and to tailor the tool to your specific testing needs. Read on to learn how k6 is structured, and how its underlying design provides the best possible reliability and load testing experience.
Unify your observability signals with Grafana Cloud Profiles, now GA
Observability has traditionally been conceptualized in terms of three core facets: logs, metrics, and traces. For years, these elements have been seen as the “pillars” of observability, serving as the foundational components for system monitoring and delivering key insights to improve system performance. However, with the exponential growth in system complexity, a more comprehensive and unified perspective on observability has become necessary.
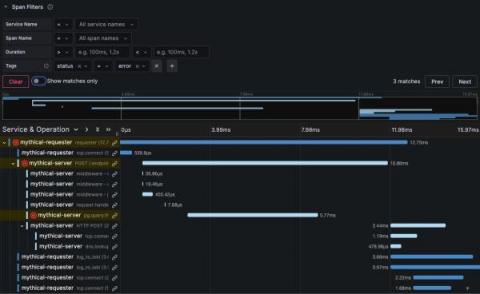
What's new in distributed trace visualization in Grafana
At Grafana Labs, we are constantly improving our feature set, and tracing is no different. Traces are often overshadowed by logs and metrics, but they’re a pillar of observability for a reason. Used correctly, organizations that can quickly and successfully follow a chain of events through a system gain a more holistic view of their systems and are better equipped to find and fix issues faster.
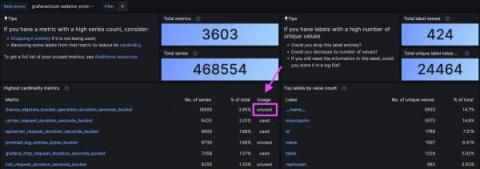
Managing Prometheus cardinality in Grafana Cloud: Adaptive Metrics FAQ
One of the most talked about topics in observability today is centered around the question of how to get more value out of the ever-increasing amount of data collected by agents, collectors, scrapers, and the like. Back in May, we announced Adaptive Metrics, a new feature in Grafana Cloud that allows you to reduce the cardinality of Prometheus metrics and the overall volume and costs of your metrics.
IoT Dashboards with Grafana and Prometheus
The Internet of Things (IoT) - is a number of physical devices connected to one network that enables the system to interact with the external world. A great deal of the work surrounding IoT is monitoring, as it’s impossible to react without knowing the situation. For example, we might build a greenhouse system for agriculture that can maintain optimal conditions for growing crops. For this purpose, we need to have sensors picking up information about the temperature and humidity.