Flux Aggregation in InfluxDB: Now or Later
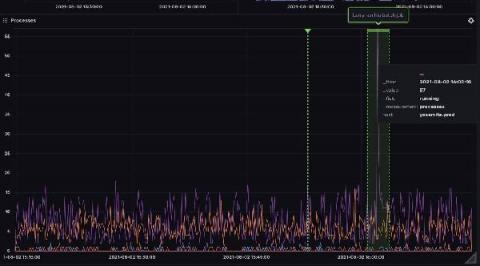
Aggregations are a powerful tool when processing large amounts of time series data. In fact, most of the time you’re going to care more about the min, max, mean, count or last values of your dataset than you will about the raw values you’re collecting. Knowing this, InfluxDB and the Flux language make it as easy as possible to run these aggregations, whenever and wherever you need to, and sometimes that leads people to running them in ways that aren’t as efficient as they could be.