Using the New Flux Usage API to Calculate Pricing for InfluxDB Cloud
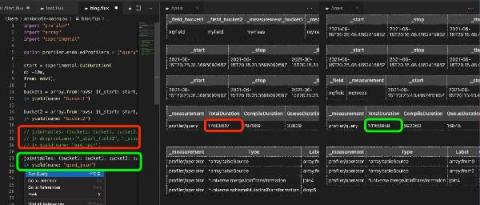
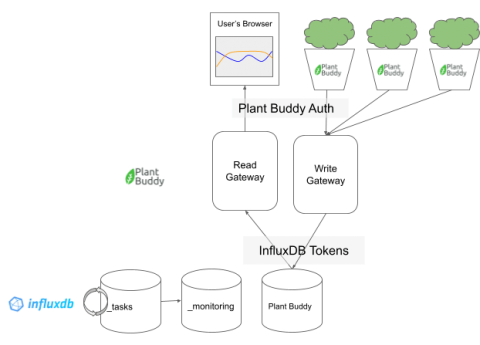
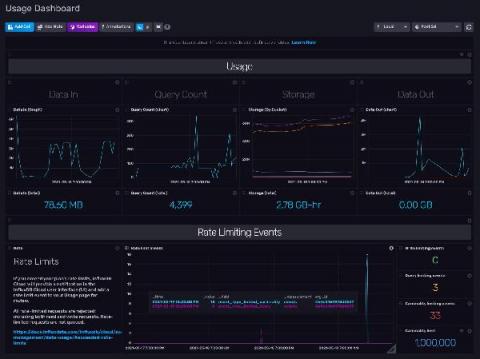
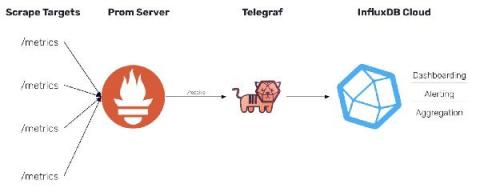
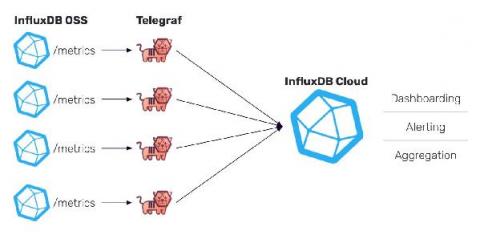
InfluxDB Cloud offers a transparent usage-based pricing model that only charges users on the work performed, with no minimums or long-term commitments. This puts YOU in charge of what you spend. However, with four separate pricing vectors, it’s not always easy to see exactly where that cost is going, or how to estimate your potential spend based on your data usage.