Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
Blog
Protecting Critical Infrastructure in Kubernetes and Rancher
“As we expand, it’s critical for our team to have both a fast and automated rollout process for each customer environment. In the end, each of our user’s access experience must be identical. Rancher is one product that’s critical to that strategy.” – Jeff Klink, VP Engineering, Cloud and Security Specialist, Sera4 Security worries keep many of us awake at night – no matter our industry.
Custom Alerts Using Prometheus in Rancher
This article is a follow up to Custom Alerts Using Prometheus Queries. In this post, we will also demo installing Prometheus and configuring Alertmanager to send emails when alerts are fired, but in a much simpler way – using Rancher all the way through. We’ll see how easy it is to accomplish this without the dependencies used in previous article.
Shipping Multiline Logs with Filebeat
Multiline logs provide valuable information for developers when troubleshooting issues with applications. An example of this is the stack trace. A stack trace is a sequence of method calls that an application was in the middle of when an exception was thrown. The stack trace includes the line in question that encountered the error, as well as the error itself.
You've launched your first Kubernetes cluster, now what?
As Kubernetes continues to grow in popularity at a staggering rate, it’s only natural more and more people want to see what all the fuss is about. We’ve seen first hand how excited people are to try it out since launching #KUBE100 (our Kubernetes beta) – we’ve had tremendous interest and some great feedback so far. If you’re reading this and you have no idea what #KUBE100 is, it’s the name we gave to our k3s-powered, managed Kubernetes beta program.
Complete Winston Logger Guide With Hands-on Examples
Logging is critical for monitoring and troubleshooting your Node.js project. The open-source Winston logger helps take a load off our shoulders by making it easier to centralize, format, enrich, and distribute the logs to fit a particular need. Winston creates custom logger instances which can be configured to act as centralized logging entities. Essentially, the internal architecture of the module decouples the actual event logging from the implementation of the storage logic.
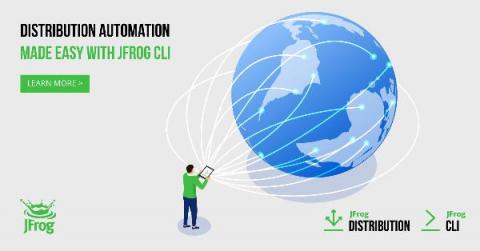
How to use JFrog CLI to Create, Update, Distribute & Delete Release Bundles
This blog post will provide you with information on how to use JFrog CLI with JFrog Distribution workflows. JFrog Distribution manages your software releases in a centralized platform. It enables you to securely distribute release bundles to multiple remote locations and update them as new release versions are produced. For those of you who are not yet familiar with the JFrog CLI, it is an easy to use client that simplifies working with JFrog solutions using a simple interface.
Summary of Icinga Virtual Meetup 2020/04
Last week we finally had our first virtual Icinga Meetup. Since we had some trouble at our very first try, we were even more excited and nervous about this. This time, after a couple of minutes it was clear that everything will go well from the technical perspective. We were prepared content-wise as well and almost all of the registered attendees showed up. Experiencing the first couple of minutes going so well was a huge relief and, in the end, the whole meeting was a great event.
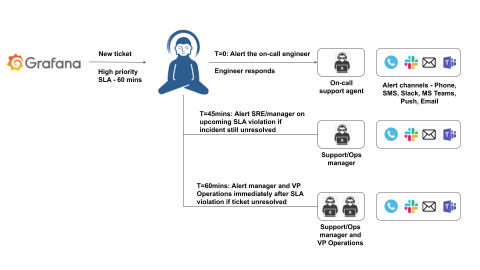
Grafana alerts and incident escalation with Zenduty
Grafana is one of the most popular open-source visualization tools that can be used on top of a variety of different data stores but is most commonly used together with Graphite, InfluxDB, Prometheus, Elasticsearch, Prometheus, AWS CloudWatch, and many others. Reliability engineers use Grafana is its ability to bring together several data sources together in a unified dashboard and increase the observability of your production systems.
Easily visualizing MITRE ATT&CK® round 2 evaluation results in Kibana
If you want to skip ahead to see the MITRE ATT&CK eval round 2 results visualized in an easy-to-configure Kibana dashboard, check it out here.