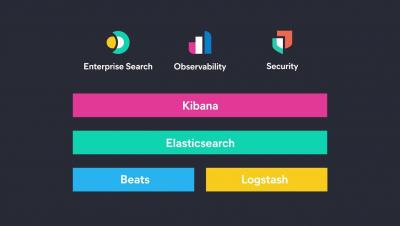
Discover in Kibana uses the fields API in 7.12
With Elastic 7.12, Discover now uses the fields API by default. Reading from _source is still supported through a switch in the Advanced Settings. This change stems from updates made to Elasticsearch in 7.11 with the extension of the Search API to include the new fields parameter. When using the new search parameter, both a document’s raw source and the index mappings to load and return values are used.