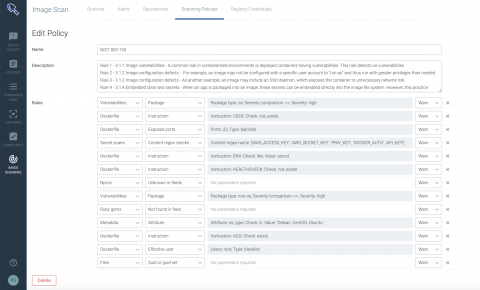
Comparing kube-proxy modes: iptables or IPVS?
kube-proxy is a key component of any Kubernetes deployment. Its role is to load-balance traffic that is destined for services (via cluster IPs and node ports) to the correct backend pods. Kube-proxy can run in one of three modes, each implemented with different data plane technologies: userspace, iptables, or IPVS. The userspace mode is very old, slow, and definitely not recommended! But how should you weigh up whether to go with iptables or IPVS mode?