Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
Latest News
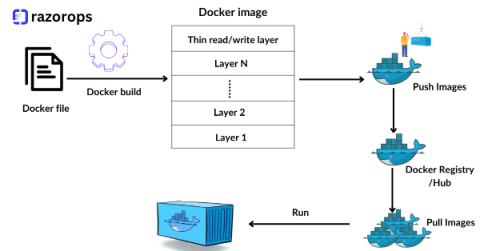
Docker File Best Practices For DevOps Engineer
Containerization has become a cornerstone of modern software development and deployment. Docker, a leading containerization platform, has revolutionized the way applications are built, shipped, and deployed. As a DevOps engineer, mastering Docker and understanding best practices for Dockerfile creation is essential for efficient and scalable containerized workflows. Let’s delve into some crucial best practices to optimize your Dockerfiles.
Striking the Balance: Tips for Enhancing Access Control and Enforcing Governance in Kubernetes
Kubernetes, with its robust, flexible, and extensible architecture, has rapidly become the standard for managing containerized applications at scale. However, Kubernetes presents its own unique set of access control and security challenges. Given its distributed and dynamic nature, Kubernetes necessitates a different model than traditional monolithic apps.
Boosting Kubernetes Stability by Managing the Human Factor
As technology takes the driver’s seat in our lives, Kubernetes is taking center stage in IT operations. Google first introduced Kubernetes in 2014 to handle high-demand workloads. Today, it has become the go-to choice for cloud-native environments. Kubernetes’ primary purpose is to simplify the management of distributed systems and offer a smooth interface for handling containerized applications no matter where they’re deployed.
Harnessing the Power of Metrics: Four Essential Use Cases for Pod Metrics
In the dynamic world of containerized applications, effective monitoring and optimization are crucial to ensure the efficient operation of Kubernetes clusters. Metrics give you valuable insights into the performance and resource utilization of pods, which are the fundamental units of deployment in Kubernetes. By harnessing the power of pod metrics, organizations can unlock numerous benefits, ranging from cost optimization to capacity planning and ensuring application availability.
Top 10 Platform Engineering Tools You Should Consider in 2024
New Feature: Deploy Your Helm Charts With Ease
How To Build Your DevOps Toolchain Effectively
Software development, the adoption of DevOps practices has become imperative for teams aiming to streamline workflows, boost collaboration, and deliver high-quality products efficiently. At the heart of successful DevOps implementation lies a robust toolchain—a set of interconnected tools and technologies designed to automate, monitor, and manage the software development lifecycle.