Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
Networks
The latest News and Information on IT Networks and related technologies.
Why ScienceLogic for Capgemini's NOC Transformation?
Unify Visibility Across Your Monitoring Tools with DX Operational Intelligence
For today’s businesses, there’s a premium on delivering innovative user experiences. As a result, stakes continue to grow for the teams in charge of supporting new digital experiences. To successfully implement modern delivery chains, IT operations need to establish comprehensive coverage that delivers unified visibility of the entire enterprise ecosystem. They need observability that spans from mobile applications to networks and mainframes.
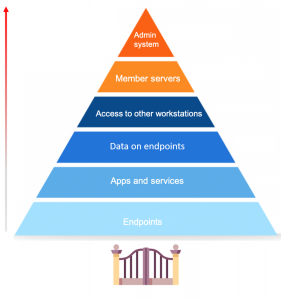
The role of endpoints in the security of your network
Endpoint security is a hot topic of discussion, especially now with so many businesses shifting to remote work. First, let’s define what endpoints are. Endpoints are end-user devices like desktops, laptops, and mobile devices. They serve as points of access to an enterprise network and create points of entry that function as gateways for malicious actors. Since end-user workstations make up a huge portion of endpoints, we’ll be focusing on their security.
Auvik Presents: Rollup & Retrospective Q2 2021
Turning Cross-Stack Correlation Into Better Collaboration | THWACK Livecast Series Session #3
DPA Virtualized Database Video
N-able Announces New Addition to Its Executive Leadership Team, Naming Jeff Nulsen as Chief Marketing Officer
Transforming Network Monitoring For The "Everything-As-A-Service" Era
Modern applications enable enterprises to scale faster with better efficiency and resilience. The main advantage of a multi-cloud/hybrid cloud infrastructure is in its highly distributed architecture that offers proximity – bringing end users closer to the service provider.
Basic DHCP concepts
Let’s step back and take a very basic look at DHCP. In fact, let’s look at the analogy of assigning a street address to your house. Usually, this is done by the local 911 dispatch office, or some other central authority. They typically use either a survey map or a latitude, longitude pair to locate you, before they assign your house numbers from a pool of available addresses, compatible with other addresses in the area.