A Guide to the Best Free and Paid DNS Services
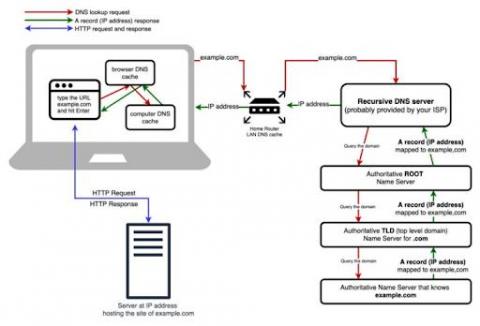
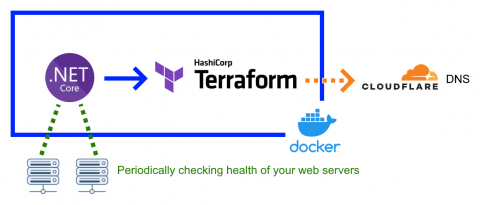
DNS stands for the Domain Name System. This system translates website names into IP addresses so that those sites could be loaded by various devices. When you are browsing the internet, you get assigned a server automatically when you are loading pages. Unless you have your own server, this might not be an ideal option. The server you use is directly responsible for the loading speed. And if it goes down, there will be no internet connection at all.