Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
API
The latest News and Information on API Development, Management, Monitoring, and related technologies.
Continuous integration for Yii2 APIs with Codeception
Continuous integration (CI) is the process of integrating changes from multiple contributors to create a single software project. A key component for a smooth CI pipeline is testing. Tests prove that the code does exactly what it says on the tin and that it’s safe to merge the code into the central repository. Tests also anticipate edge cases and ensure that the code handles such cases in a deterministic manner.
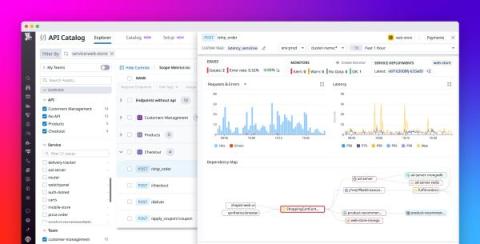
Manage API performance, security, and ownership with Datadog API Catalog
Today’s modern applications are made up of thousands of loosely connected private and publicly exposed APIs, each serving a specific function. This dynamic API landscape, in combination with the decentralized nature of microservice development, can be overwhelmingly challenging to manage—let alone govern or secure adequately. API sprawl is often created as a result, leading to fragmented or nonexistent internal API documentation, knowledge bases, and toolsets.
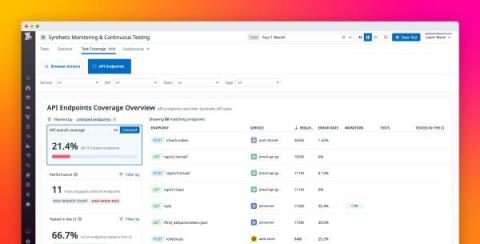
Improve your API test coverage with Datadog Synthetic Monitoring
As your applications grow, your teams may be faced with managing a complex, expanding mesh of potentially thousands of loosely connected APIs—each one a new point of failure that can be difficult to track and patch. API sprawl comes naturally in rapidly expanding, distributed applications, and the difficulty of maintaining centralized knowledge and toolsets for your APIs creates friction when teams need to leverage APIs they don’t own.
Testing a Spring Boot API with SpringBootTest and CircleCI
When it comes to building and delivering modern web applications, the importance of continuous integration cannot be overemphasized. With the rapid pace of software development, ensuring that every change in your codebase is thoroughly tested and seamlessly integrated into your project is essential for maintaining a robust and dependable application.
The Unplanned Show, Episode 15: PagerDuty APIs with Nakul Bhagat
Query 3rd Party API Datasets in Real Time with Cribl Search
In today’s world of relentless data growth, security-relevant logs represent a small snapshot of an organization’s overall environment. Teams are beset with a variety of data types, including performance metrics and traces, asset configuration and state, audit logs, and much more. On top of that, teams are expected to scan all of this to compare against industry best practices and join this data with logs and metrics for added context.
Monitor your Boomi integrations with Kitepipe's offering in the Datadog Marketplace
Boomi is a cloud-based integration platform that helps customers connect their applications, data sources, and other endpoints. But monitoring and troubleshooting Boomi Atoms—the runtime engines for Boomi integration processes—and the applications connected to them can be a challenge. Boomi automatically purges logs after 30 days, and users must frequently correlate data from various disconnected sources for visibility into their Boomi processes.