Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
Search
Announcing OpenSearch: Doubling Down on Open Source
Today, I’m excited to officially announce our support for the OpenSearch project, the new fork of the Elasticsearch and Kibana codebases. As we previously shared, Logz.io has the utmost commitment to its customers and the community to ensure that these open-source technologies will prosper by being built for the community and guided by the community.
How to build a facial recognition system using Elasticsearch and Python
Have you ever tried to search for objects in images? Elasticsearch can help you store, analyze, and search for objects in images or videos. In this quick tutorial, we’ll show you how to build a system for facial recognition with Python. Learn more about how to detect and encode facial information — and find matches in search.
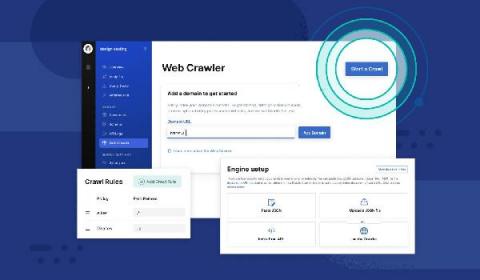
How to troubleshoot the Elastic App Search web crawler
In case you hadn’t heard, we recently released a brand new web crawler for Elastic App Search. The web crawler provides a simple way to ingest publicly available web content and make that content instantly searchable on your website. Configuring the web crawler to start ingesting data from your website is super easy — it’s just a matter of a few clicks. This sounds great, but what if after crawling there are no pages being indexed or you feel some pages are missing?
Time-based scaling of Enterprise Search on Elastic Cloud
Does your Elastic Enterprise Search Cloud deployment follow a predictable usage pattern? You can automatically scale up and down your deployment on a schedule to achieve optimal performance and reduce operating costs. In this article we show you how to use the Elastic Cloud API to change how many Enterprise Search nodes you’re running. We call these APIs from a cron job to achieve hands-free, time-triggered autoscaling.
Power of Search
How to Optimize Your Elasticsearch Queries Using Pagination
Consider for a moment that you are building a webpage that displays data stored in Elasticsearch. You have so much information in your index that your API Gateway cannot handle it all at once. What you’ll need to do is paginate your results so that the client can have a predictable amount of data returned each time. Before paginating your results with your client, you will need to know how to paginate data in your backend storage.
Search and replicate across regions and cloud service providers with Elastic Cloud
We are excited to announce the general availability of cross-cluster search and replication on Elastic Cloud. These two features allow you to search and replicate data across clusters in different regions and cloud service providers globally, making it possible to: Be sure to dive in and learn more about the features below! Cross-cluster search lets you search remote clusters across multiple regions and cloud service providers. When you break down regional data silos, you can get insights faster.
How to manage Elasticsearch data across multiple indices with Filebeat, ILM, and data streams
Indices are an important part of Elasticsearch. Each index keeps your data sets separated and organized, giving you the flexibility to treat each set differently, as well as make it simple to manage data through its lifecycle. And Elastic makes it easy to take full advantage of indices by offering ingest methods and management tools to simplify the process.
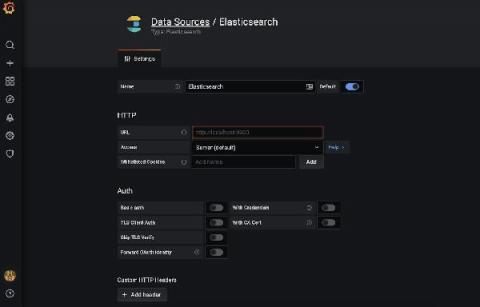
Why we're partnering with Elastic to build the Elasticsearch plugin for Grafana
As I’ve often talked about before, we have a “big tent” philosophy at Grafana Labs. We believe our users should determine their own observability strategy and choose their own tools; Grafana allows them to bring together and understand all their data, no matter where it lives. In practice, that means that we want to support data sources that our users are passionate about.