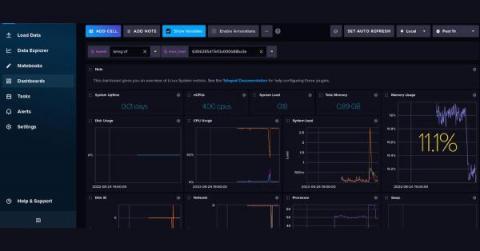
Unified Observability: Announcing Kubernetes 360
Ask any cloud software team using Kubernetes (and most do); this powerful container orchestration technology is transformative, yet often truly challenging. There’s no question that Kubernetes has become the de-facto infrastructure for nearly any organization these days seeking to achieve business agility, developer autonomy and an internal structure that supports both the scale and simplicity required to maintain a full CI/CD and DevOps approach.