Introduction to Giraffe
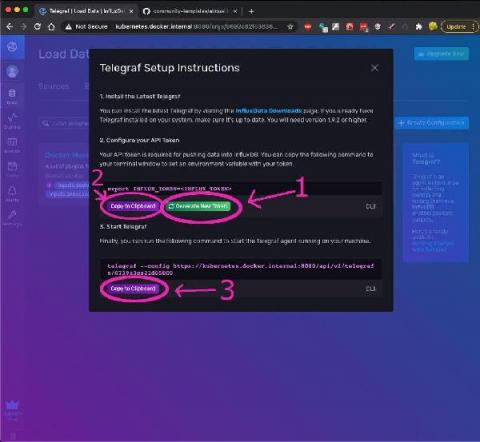
Giraffe is InfluxData’s graphing library, built to use and graph the data coming from InfluxData’s time series database, InfluxDB. Yes, there are other graphing libraries available; but ours is the only one purpose-built to graph line protocol without having to convert it. Plus, we have lots of great features, like legends and colorization, without much configuration. So, how to get started?