Operations | Monitoring | ITSM | DevOps | Cloud
August 2022
How to Save Costs With IT Monitoring
Why Parkview Health Chose Zenoss
The Enemy of Efficiency is the Lack of Automation
Emergence of cloud desktops
Cloud Governance vs. Cloud Management
Measuring Cloud Instance Costs for FinOps
Achieving cost savings is one of the main drivers for cloud adoption. But for most companies, controlling cloud spend is much more challenging than anticipated. In a recent survey, 94% of IT decision makers report they are overspending in the cloud. Our own survey on cloud costs revealed 90% of executives say better cloud cost management and cost reduction is a top priority.
BWI optimizes SAP use with USU software asset management
How to monitor Couchbase with Google Cloud Ops
What Are Privacy Acts? And Why Are They Important for Your Business?
Rackspace IT Tool Consolidation with Zenoss
FinOps: Measuring Allocatable Cloud Spend
Cloud services are the number one source of unexpected overspending for companies today. As a result, cloud financial management is a major focus for most organizations. But how do you track the success of cloud efficiency? Full allocation of multicloud costs is a critical component for understanding your actual cloud services usage, establishing cloud cost management ownership, and creating accurate budgets and forecasts at the line of business, project, application and even team levels.
How to Drive IT Efficiencies While Reducing Spend
How Does Unified Monitoring Reduce MTTR?
Monitor your Microsoft Azure VMs featuring Ampere Altra Arm-based CPUs with Datadog
As organizations continue to expand their cloud footprint, managing costs without risking application performance is a priority. Because of this, Arm processors have become popular for their efficient, cost-effective processing power. Microsoft Azure’s new series of Azure Virtual Machines are powered by Ampere Altra Arm-based processors, which provide excellent price performance for scale-out and cloud-native workloads.
Simplify IT Management with Hyperconverged Infrastructure
9 Cloud Cost Mistakes You Don't Know You're Making
Elastic Observability helps monitor your Azure workloads on the new Arm-based VMs
Microsoft Azure’s recently launched new Azure Virtual Machines (VMs) feature the Ampere Altra Arm-based processor. These new VMs are engineered to efficiently run horizontally scalable workloads such as web servers, application servers, and open source databases. They deliver excellent price-performance and represent an important addition to Microsoft Azure's portfolio of instance types.
Deploying a Web App in any cloud using Terraform and Multy
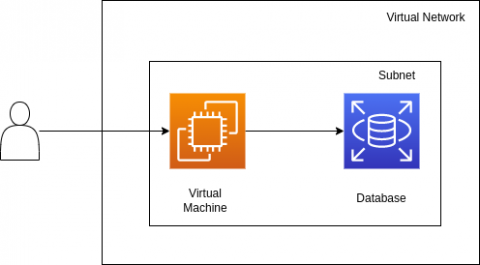
In this tutorial, we'll deploy a simple web app to the cloud of your choice - composed of a database and a virtual machine where the frontend code will run. So that the configuration is reusable and consistent, we'll write it in Terraform. Usually Terraform configurations are cloud-specific, and changing clouds requires a complete rewrite. In this case, so that you can reuse the same configuration across clouds, we'll be using Multy.
Qoddi for open source projects
At Qoddi, we are strong advocates and sponsors of open-source projects, and with the recent decision from Heroku to stop offering free plans (used by a lot of open-source developers), we felt the importance of having an alternative ready to keep those projects running. Qoddi's infrastructure is compatible with most of Heroku's buildpacks and we wrote a guide to migrate a project from Heroku.
Privacy vs Anonymity: What's the Difference and Why They Matter
15 Essential Container Orchestration Tools For 2022
Getting Started with Sematext Cloud
What Is Amazon Redshift?
How to Fix Poor Azure Latency
Learn how to reduce your latency and get better network performance from the popular cloud service provider.
Simplify Cloud Data Onboarding with the NEW Data Manager
Monitor 70,000 Managed Resources in a Single Pane of Glass
Deploying a dockerized .NET Core app to an Azure container instance
In this tutorial, you will learn how to build a custom ASP.NET Core container with Docker and host the container image on Azure Container Registry, a platform owned by Microsoft that allows you to build, store, and manage container images in a private registry. At the end of this tutorial, you will be able to apply the knowledge gained here to link your container image on the Microsoft Azure registry with a web app service and launch your application.
Data Breach Prevention Methods in Cloud Computing
Why Choose Cloud-Based Asset Management Software in 2025?
Get the Most Out of Serverless for Fleet Management Apps
You’ve probably seen Rush Hour, a logic puzzle where you have to slide cars and trucks out of the way to steer the red car towards the exit. In real life, when your customers are responsible for tracking hundreds or thousands of data points from dozens of valuable, mission-critical sensors, you’re tracking engine speed, network signal level, distance from the RF, and more—and not just through traffic but across continents.
What is Azure Advisor?
Azure Advisor analyzes your configurations and usage telemetry and offers personalized, actionable recommendations to help you optimize your Azure resources for reliability, security, operational excellence, performance, and cost. Azure Advisor is a free service and can be accessed via the GUI on the Azure portal where recommendations are collated and can be manually examined. Azure Advisor makes recommendations for potential improvements in several areas, including.
Partner Talk: Chris Free, CEO of Chromatic
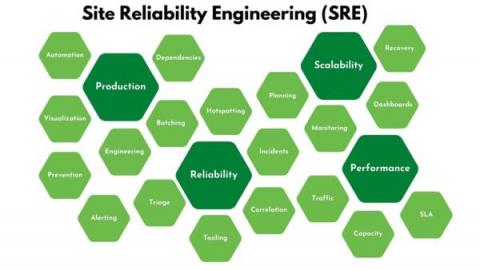
Site Reliability Engineering: Definition, Principles & How It Differs From DevOps
Site crashes and outages can cost hundreds of thousands in lost revenue and inconvenience users. Site Reliability Engineering helps build highly reliable and scalable systems, particularly important for companies that depend on their software to support their customers performing critical operations. Hiring a Site Reliability Engineer is the best way to ensure a software system stays up and running at all times. Not only will they help manage infrastructure and applications, but they'll also be able to advise on how to scale a business as it grows - keeping downtime and incidents at a minimum!
5 Things A Successful VPE And CTO Should Do Every Day
Why and How to Monitor AWS Elastic Load Balancing
When building systems that need to scale above a certain number of users, we usually can’t stay on one machine. This is where cloud providers like AWS usually come into play. They allow us to rent VMs or containers for small intervals. This way, we can start a few different machines when more traffic hits, and when it goes down later, we can simply turn off our extra capacity and save money. The question is, how does all this traffic get to our new machines? AWS Elastic Load Balancing!
How to Secure Your Data in the Cloud
We’ve entered a time when hard drives are becoming less important than data speeds, syncing, and remote storage. More and more end-users are saving their files in the cloud for convenience, safety, and cost savings. That said, some people still have concerns about cloud computing -- namely around security. How safe are files that are stored hundreds or thousands of miles away, on some other organization’s hardware?
Is Online Privacy Dead? Why Companies Infringe on Your Digital Rights
Shine Some Light on Your SNS to SQS to Lambda Stack
The combination of SNS to SQS to Lambda is a common sight in serverless applications on AWS. Perhaps triggered by messages from an API function. This architecture is great for improving UX by offloading slow, asynchronous tasks so the API can stay responsive. It presents an interesting challenge for observability, however. Because observability tools are not able to trace invocations through this combination end-to-end. In X-Ray, for example, the trace would stop at SNS.
The 2022 Managed Kubernetes Showdown: GKE vs AKS vs EKS
Kubernetes may provide an abundance of benefits, but those who are using it may be well aware that it often requires quite a bit (or even a lot!) of effort and skill to run the platform independently. So – rather than having to put up with it on their own, organizations are able to pay for a managed Kubernetes service instead. This is where Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), and Amazon Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS) come in.
SaaS Monitoring Best Practices
How Can Startups Affordably Embrace Cybersecurity?
AWS US-EAST-1 Outage... Again
Getting Started With Azure Database for PostgreSQL
Troubleshooting AWS EC2 Slowness
Among the 200+ fully features services that Amazon Web Services (AWS) offers, Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2) is the most popular. In the recent eG Innovations and DevOps Institute survey of 900+ IT professionals, cloud instances were the most commonly used cloud service, with 63% usage among respondents.
VS Code integration with Ocean for Apache Spark
Automatically deploy REST APIs with Lambda authorizers using AWS CDK
This is the second tutorial in a two-part series. You can also learn how to automate AWS Lambda function deployments to AWS CDK.
Your Cloud Provider Will Fail You Eventually
Cloud has become the de facto way to build infrastructure, meaning cloud providers end up in charge of a significant amount of the apps we use every day. From the likes of Netflix, Slack, Ring and Doordash running on AWS or PayPal, Twitter and HSBC on GCP, it's easy to see how impactful a failure of any type can be. Let's look at some of the issues that have happened recently that have led business to consider how dependent they are on a single provider.
Distributed tracing and correlation through Service Bus messaging
What Is Function as a Service (FaaS)
There are numerous types of services and processes in place to make software development more accessible and efficient for programmers. One ready-for-launch service developers can access remotely is Function as a Service, abbreviated as (FaaS).
FOSS for Dummies: What Is Free and Open-source Software?
Cloud User Hub will help partners tame the Microsoft Cloud
We’re pleased to announced the launch of N-able Cloud User Hub, following the acquisition of Spinpanel in July of this year. N-able Cloud User Hub is a multi-tenant Microsoft 365 management and automation platform built for Microsoft Cloud Solution Providers and allows users to automate the management and security of all Microsoft tenants, users, and licenses.
Sustainable Technology: Can Clouds Save The Planet?
Advanced Debugging and Monitoring for Serverless Backends
Serverless backends have different monitoring challenges when compared with traditional applications, mostly due to the distributed and proprietary nature of serverless. Making monitoring and debugging efficient for serverless requires a unique set of tools and techniques. In this article, we’ll discuss the challenges of debugging serverless backends and how to utilize third party tools to improve the monitoring process.
Quick Bytes - Execution Tags
Lumigo for Colorcast: A Game of Metrics
Getting Started With Azure Database for PostgreSQL
How To Handle Untaggable And Untagged Cloud Spend
Self-hosted versus cloud-based mobile app testing
Testing is a vital part of the mobile app development process. Your team can use testing to evaluate the quality, security, and reliability of mobile apps before releasing them to your users. Users who expect their applications to be highly performant and intuitive. There are two ways DevOps teams can perform testing for mobile apps: on-premise (also called self-hosted) or in the cloud. But which of these is the best option for your team?
Progressive deployments of Kubernetes applications
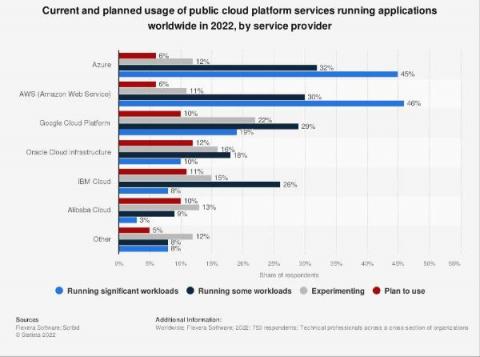
State of Cloud Cost Report 2022
Cloud migration efforts continue to grow today as organizations move into a post-pandemic work environment. According to McKinsey & Company, by 2024, most enterprises aspire to have $8 out of every $10 for IT hosting go toward the cloud. In a survey by Morgan Stanley, CIOs say cloud computing will see the highest rate of IT spending growth in 2022.
AWS Monitoring Tool
Automate AWS Lambda function deployments to AWS CDK
When you build a cloud-based application, you can choose to deploy the resources using the GUI (Graphical User Interface) or CLI (Command Line Interface) provided by the cloud provider. This approach can work well with just a handful of resources, but as the complexity of your application increases, it can become difficult to manage the infrastructure manually.
Amazon Photos Alternative? The Good, the Bad, and More Private Options
Seven Tools to Help You Become a Better Serverless Developer
Serverless technologies let us do more with less effort, time and energy. They let us focus on creating user value and let the cloud handle undifferentiated heavy-lifting like scaling and securing the underlying infrastructure that runs our code. Serverless technologies have allowed me to accomplish tasks as a solo engineer that used to take a whole team of engineers to accomplish, and I’m able to complete these tasks in a fraction of the time and cost to my customers.
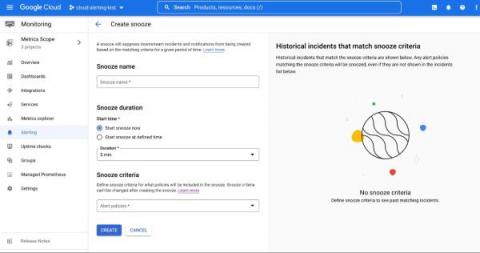
Snooze your alert policies in Cloud Monitoring
Does your development team want to snooze alerts during non-business hours? Or proactively prevent the creation of expected alerts for an upcoming expected maintenance window? Cloud Alerting in Google's Cloud operations suite now supports the ability to snooze alert policies for a given period of time. You can create a Snooze by providing specific alert policies and a time period. During this window, if the alert policy is violated, no incidents or notifications are created.
Intelligent Instance Selection for Your Kubernetes Workloads
How Cloud Network Monitoring Is Critical To Business Success
A rising number of businesses are adopting and utilizing cloud services and capabilities with remarkable success. But embracing cloud tools and services often brings unexpected changes for business leaders and IT teams, especially because of the way in which cloud adoption has altered how networks are monitored and managed.
How to retrieve Azure Key Vault Secrets using Azure Functions (Part II)
Why devops needs a better approach to cloud networking
A full-stack networking platform with machine learning, autonomous capabilities, and multicloud support allows devops engineers to focus on what matters most—building applications. The promise of digital transformation is enabling businesses to magnify competitive advantages, create new revenue streams, and improve customer experiences.
Migrating from VMware to an open-source private cloud in financial services
This is part one of a two part blog series on open source based private cloud for financial services. This blog describes the need for a cost-effective private cloud to execute a successful hybrid cloud strategy. It also shares a comparison between proprietary and open source based private cloud platforms.
3 Must-Use Strategies To Make Better SaaS Pricing Decisions
Understanding Cloud Services: IaaS, SaaS, and PaaS
Cloud services have skyrocketed in popularity in the past few years, providing a vast array of resources as well as a cost-effective path for the migration from on-premises servers to the cloud. In fact, cloud services are handling all the computing needs of many businesses. It’s very likely you’re already using cloud services and will continue to use more as time goes on.
Cycle Podcast | EP 15 | Darren Shepherd | The State of Running Containers in the Wild
Why a big bang approach is the wrong cloud strategy
Despite all the hype from the big cloud providers the truth is that most organisations rely on hybrid infrastructures now and will do so for the foreseeable future. Typically, this includes on-premises infrastructure and at least two public cloud providers. This is not a step on a journey to being 100 per cent cloud, it is the strategic destination many have chosen.
5 Common Cybersecurity Mistakes You Can Easily Prevent
Everything You Need to Know About Cloud Database (SaaS, DbaaS, IaaS, PaaS, And Others)
The demand for cloud services is rising. Databases have been popular tools for a long time. However, the landscape is changing, with cloud databases becoming increasingly popular.
Top Tips for NodeJS and Debugging on AWS Lambda (Part 2)
This is the second post in a 2 part blog series on debugging, monitoring and tracing NodeJS Lambda applications. If you haven’t yet seen part 1, check it out here (it’s a great read!) Now let’s get back into our post with one of the most commonly experienced issues when it comes to Lambda functions, Cold Starts.
The regulation driving multi-cloud adoption
Cloud computing can bring many benefits to financial services companies such as increased speed and agility, easier innovation and scalability. It is no wonder then that cloud adoption is set to continue increasing with 54% of financial services companies expected to have more than half of their entire IT footprint in public clouds in the next five years. However, despite the benefits that this can bring for financial services, it also brings a new set of challenges for financial market stability.
How to launch Confidential VMs on Azure
Is cloud computing immune from economic downturns?
IT is now seen as integral to business rather than a cost center ripe for layoffs. Technology, people, and culture are worth protecting during economic contractions. A recent piece in Silicon Angle by Paul Gillin said out loud what I see firsthand: Cloud spending seems immune to budget reductions during contractions in the economy.
ALB vs. ELB
How Customers Drive Our Continuous Innovation
RESOLVE '22: How to get multi-cloud done right
Multi-cloud is inevitable. With AIOps, struggling in its complexity doesn’t need to be. Business technology stacks don’t appear out of a vacuum. For the modern cloud-enabled, cloud-dependent company (that is to say, most of them), the look from the inside looks more like an ongoing evolution than a monolithic choice.
Why Your Legacy Cloud Cost Tools Aren't Cutting It
Quick Bytes - Lumigo Alerts
Lumigo for Colorcast: A Game of Metrics
Monitor Your AWS AppSync GraphQL APIs with Simplicity
TL;DR: Dashbird launched observability for AWS AppSync. Additionally to AWS Lambda, SQS, DynamoDB, API Gateway, ECS, Kinesis, Step Functions, ELB, SNS, RDS, OpenSearch, and HTTP API Gateway you can now get detailed insights and metrics in the Dashbird app for AWS AppSync. Since Facebook released its previously internally used query language GraphQL in 2016, it has seen an outstanding increase in adoptions for all kinds of applications.
Why it makes sense to invest in a hybrid cloud future
A cloud-first strategy is increasingly seen as the standard way to achieve efficient business operations. As the favoured approach of new start-ups and expanding businesses wanting to benefit from the flexibility and resilience of the cloud, it’s little wonder that foundational cloud services saw a revenue growth of 38.5% in 2021 according to IDC. It looks like a fantastic package from the outside.
Technical debt does not disappear
Cloud is currently seen by some of the clients I speak with, as the answer to associated technical debt. Technical debt is like any other debt – growing year-on-year, month-by-month. Simply relocating a workload from your dated compute stack to someone else’s system or service is not a panacea to every business-led postponement.
Cloudability Pricing: How Much Does Cloudability Cost?
What is AWS Kinesis?
Splunk Cloud Migration Made Easy with Splunk Cloud Migration Assessment App
Using BAM from Azure Synapse Pipelines
Cloud certifications for the security of your data
More and more companies around the world are using cloud solutions to run their applications, software or to store their data. But what about cloud compliance? The democratisation of the cloud is not surprising as it provides access to virtual data storage where companies no longer need to buy or maintain their own IT infrastructure. However, with cloud solutions, the security of user data should not be overlooked. There are cloud certifications and regulations that can help you in your choice.
VMware Image Builder Helps Verify Customized, Secure Software for Any Platform on Any Cloud
With the emergence of new programming languages, libraries, packaging systems, and dependencies, the open source landscape has become more diverse. At the same time, companies are finding it more and more complex to package and deliver open source software. This creates a massive challenge for independent software vendors (ISVs), large enterprises, and other organizations that need to control their software supply chain lifecycles while adhering to industry standards and best practices.
GigaOm Radar: Spot Leads the Way in FinOps Tools
Kubernetes is not the only one. Overview of AWS ECS
In part two, I will cover: Microservices Architecture Overview: New Challenges for Monolithic Architecture As an application grows, so does the amount of code written. This can quickly overwhelm the development environment every time it needs to be opened and run. As you must deploy everything in one place, this approach means that the transition to another programming language, or other technologies becomes a big problem.
New! Common Automated Diagnostics for AWS Users
Today’s modern cloud architectures centered on AWS are typically a composite of ~250 AWS services and workflows implemented by over 25,000 SaaS services, house-developed services, and legacy systems. When incidents fire off in these environments—whether or not a company has built out a centralized cloud platform—distinct expertise is often a necessity.
EKS Pricing 101: A Guide To Understanding EKS Costs
Is Cybersecurity Hard? The Basics Made Easy To Understand
5 best practices for cloud cost optimization that you should never miss- Site24x7 CloudSpend
Before we jump into cloud cost optimization, let us address the elephant in the room. Businesses are moving to the cloud but are struggling with unpredictable cloud bills. If you are a business owner who has moved to the cloud recently, you need to understand each cloud touchpoint and get a transparent view of your cloud services. When it comes to cloud cost optimization, there are many tools and techniques that organizations can adopt. Most of these can only take you so far.
Introduction to Cloud Native
User experience is the pinnacle of cloud technology. With cloud data centers handling 94 percent of all workloads, cloud optimization is vital. Users need fast, agile, scalable, and stable solutions over the long term. But how do you build these solutions? This is where cloud-native technology comes in. Cloud native computing provides the foundation for building, designing, running, and managing applications in the cloud.
Top Tips for NodeJS Tracing and Debugging on AWS Lambda (Part 1)
In this two post series, we are going to explore some ways to trace and debug NodeJS Lambda applications. Delving into some methods to look further into resources utilized to and some methods to optimize code. AWS Lambda, an event-driven compute service first introduced roughly eight years ago, changed how we build out cloud applications as an industry.
New improvement: global settings in console
At Platform.sh, we are committed to making your development and deployment experience as smooth and seamless as possible. As part of this effort, we regularly listen to your feedback to see how we can improve things. One of those things: is how complex it can be to configure environment or project settings from the Console. That is why we decided to regroup all settings pages together so that they’re easily accessible from a single location.
How to retrieve Azure Key Vault Secrets using Azure Functions (Part I)
Cloud vs Data Center: Overview for Businesses
The debate of cloud vs data center looms large for businesses when determining how to best store data. In past years, the trend has leaned more toward the growth of remote solutions using the cloud. Yet, data centers are still relevant. Gartner states that spending on data center infrastructure is expected to grow 6% by the end of 2021. Cloud storage and data centers both possess unique features that allow you to achieve your organization’s data goals.